Hi everyone👋🏻, I want to share with you all how to build Android apps using the latest trends in 2023.
What is Android?
Android is an open source operating system based on the Linux kernel, developed by Google. It is widely used on a variety of devices including smartphones, tablets, TVs and smartwatches.
Currently, Android is the most used mobile operating system in the world; according to statcounter, with the past 12 months as a sample, Android has a market share of 70.77%.
Next, I will mention a list of tools, libraries, architectures, guidelines and other utilities that I think are very important for building modern apps on Android.
Kotlin ❤️

Kotlin is a programming language developed by JetBrains. Recommended by Google, it was officially announced in May 2017 (see the publication here). It is a modern programming language with compatibility with Java that can run on the JVM, which has made its adoption very fast in Android application development.
Whether you are new to Android or not, you should consider having Kotlin as your first choice, don't swim against the tide 🏊🏻😎, Google announced this in Google I/O 2019. With Kotlin you will be able to use all the features of a modern language including the powerful Coroutines and using modern libraries developed for the Android ecosystem.
The official Kotlin documentation is here
Jetpack Compose 😍

Jetpack Compose is the modern toolkit recommended by Android for building native UI. It simplifies and accelerates UI development on Android.
Jetpack Compose is part of the Android Jetpack libraries, using the Kotlin programming language to easily build native user interfaces. At the same time, it also integrates with other Android Jetpack libraries like LiveData and ViewModel making it easier to build reactive and maintainable Android apps.
Some key features of Jetpack Compose include:
- Declarative UI.
- Customizable widgets.
- Easy integration with existing code.
- Real-time previews.
- Improved performance.
Resources:
Android Jetpack

Jetpack is a set of libraries to help developers follow best practices, reduce boilerplate code, and write code that works consistently across different versions and devices so developers can focus on the code they care about.
Some of its most commonly used tools are:
Material Design
Material Design is an adaptable system of guidelines, components, and tools that support the best practices of user interface design. Backed by open-source code, Material Design simplifies collaboration between designers and developers, and helps teams quickly build beautiful products.
Material Design is supported by designers and developers from Google, it will give us a guide for our UI/UX work for Android, Flutter and Web.
Currently, the last version of Material Design is 3, you can see more here.
Clean Architecture
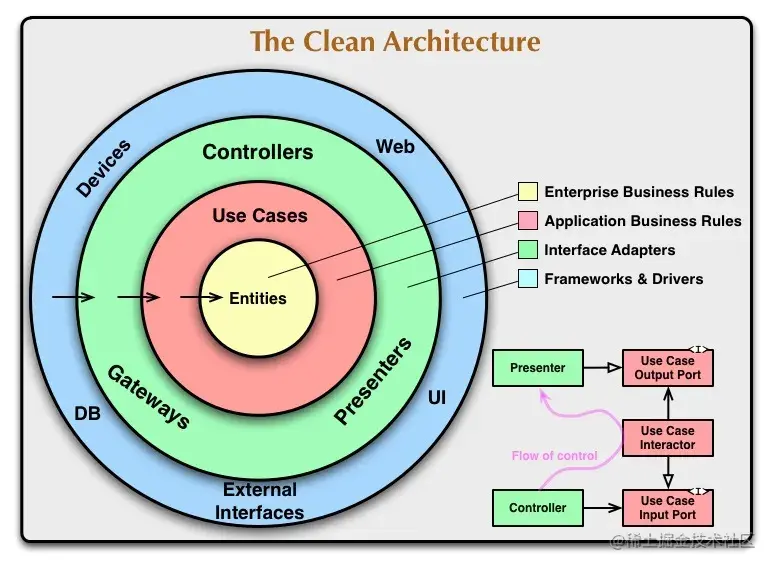
The concept of Clean Architecture was proposed by Robert C. Martin. It is based on separating responsibilities by dividing software into different layers.
Characteristics:
- Independent of frameworks.
- Testable.
- Independent of UI.
- Independent of database.
- Independent of any external agency.
Dependency Rules
The blog post Clean Architecture describes the dependency rules well.
The overriding rule that makes this architecture work is The Dependency Rule. This rule says that source code dependencies can only point inwards. Nothing in an inner circle can know anything at all about something in an outer circle. In particular, the name of something declared in an outer circle must not be mentioned by the code in the an inner circle. That includes, functions, classes. variables, or any other named software entity.
Clean Architecture blog post
Clean Architecture in Android System
- Presentation Layer: Activities, Fragments, ViewModels, other view components.
- Domain Layer: Use cases, entities, repositories, other domain components.
- Data Layer: Repository implementations, mappers, DTOs, etc.
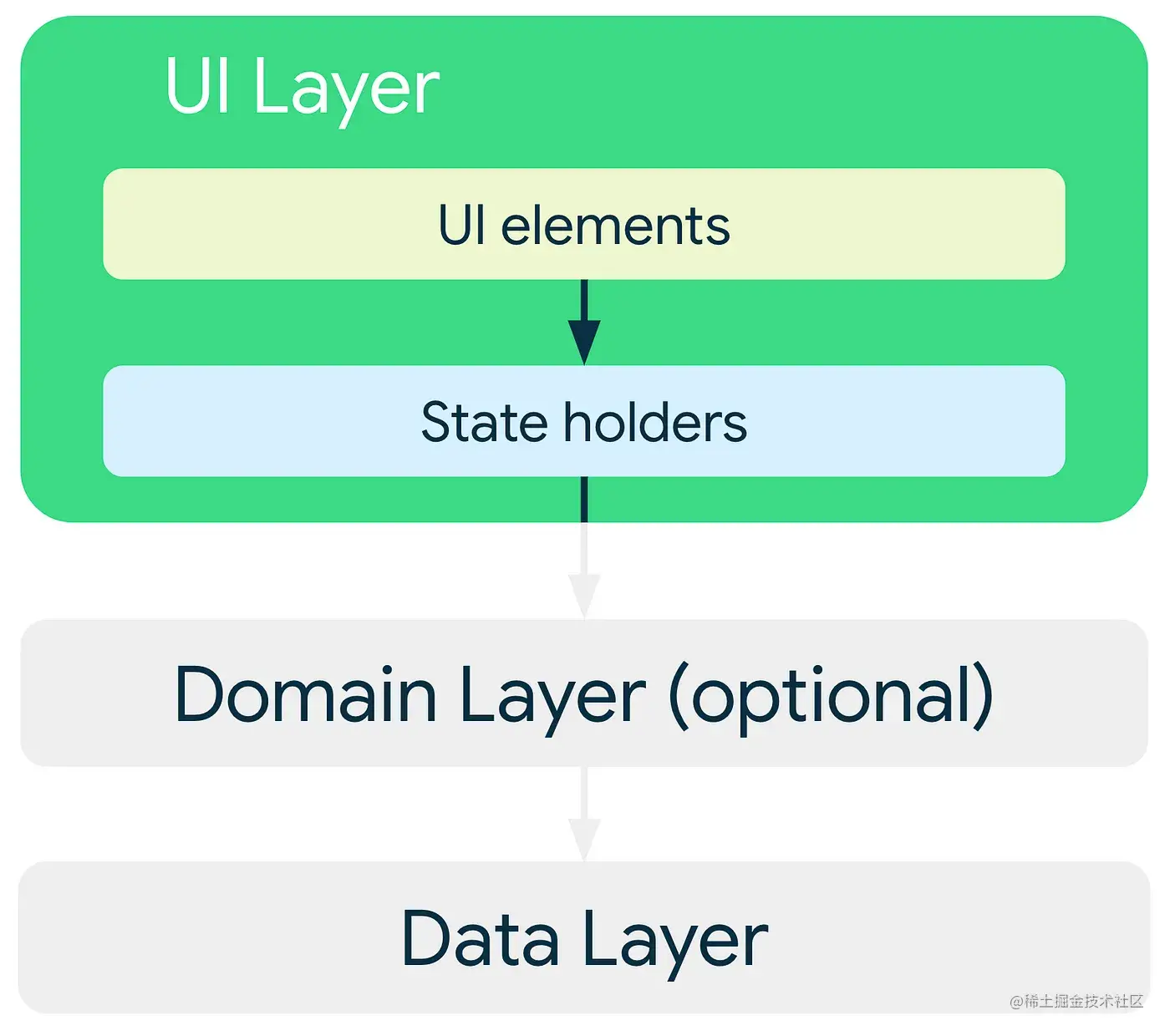
Architectural Patterns for the Presentation Layer
Architectural patterns are higher-level strategies aimed to help design a software architecture featuring solutions to common architectural problems within a reusable framework. Architectural patterns are similar to design patterns but operate at a higher level, addressing more global issues like the overall structure of a system, the relationships between components, and the ways data is handled.
In the Presentation Layer we have some architectural patterns which I want to highlight:
- MVVM
- MVI
I don't want to explain them one by one because you can find too much related information on the internet.
Additionally, you can also take a look at the App Architecture Guidance
Dependency Injection
Dependency injection is a design pattern that allows a client to obtain its dependencies from an external source rather than creating them itself. It is a technique for implementing inversion of control (IoC) between objects and their dependencies.
Modularization
Modularization is a software design technique that allows you to divide an application into independent modules, each with its own functionality and responsibilities.
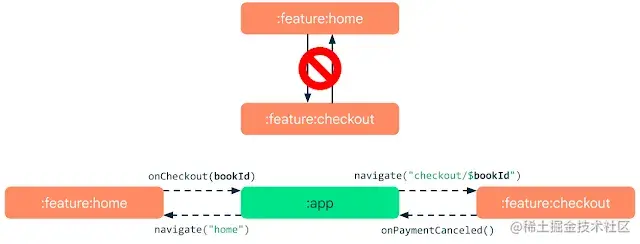
Benefits of Modularization
Reusability: Having independent modules allows them to be reused across different parts of the app or even in other apps.
Strict visibility control: Modules allow you to easily control what you expose to other parts of your codebase.
Customizable delivery: Google Play Feature Delivery uses app bundles to enable advanced features of your app to be delivered conditionally or on-demand.
Scalability: Functionality can be added or removed without impacting other parts of the app due to independent modules.
Maintainability: Having the app divided into independent modules, each with its own functionality and responsibilities, makes it easier to understand and maintain code.
Testability: Having independent modules allows them to be isolated for testing, making detection and fixing of bugs easier.
Architectural improvements: Modularization helps improve the architecture of the app giving it better organization and structure.
Improved collaboration: Independent modules allow developers to work simultaneously on different parts of the app without interference.
Build times: Some Gradle features like incremental builds, build caching or parallel builds can take advantage of modularization to improve build performance.
See more in the official documentation.
Networking
Serialization
In this section I want to mention two tools that I think are important: Moshi widely used together with Retrofit, and Kotlin Serialization which is Jetbrain's Kotlin team bet.
Moshi and Kotlin Serialization are serialization/deserialization libraries for Kotlin and Java that allow you to convert objects to JSON or other serialization formats, and vice versa. Both provide a user-friendly interface optimized for use in mobile and desktop apps. Moshi focuses primarily on JSON serialization while Kotlin Serialization supports various serialization formats including JSON.
Image Loading
To load images from the internet there are several third party libraries that can help handling that process. Image loading libraries do a lot of the heavy lifting for you - they handle both caching (so you don't download an image multiple times) and network logic to download the image and display it on the screen.
Reactivity / Thread Management
When we talk about reactive programming and asynchronous processes our first choice are Kotlin Coroutines; with suspend functions and Flow we can satisfy all these needs. However, I think it's important to highlight in this section the importance of RxJava even in Android application development. For those of us who have been working on Android for several years, we know RxJava is a very powerful tool with a lot of capabilities for handling data streams. Today I still think RxJava is a viable alternative to consider.
- Kotlin Coroutines: [suspend functions/Flow Api] (So happy to have ❤️)
- RxJava
Local Storage
When building mobile apps it's very important to have the ability to persist data locally like some session data or cache data among others. Choosing the right storage option depending on your app needs is important. We can store unstructured data like key-value or structured data like databases. Remember this point didn't mention all the local storage types we have available (like file storage), just the tools that allow us to save data.
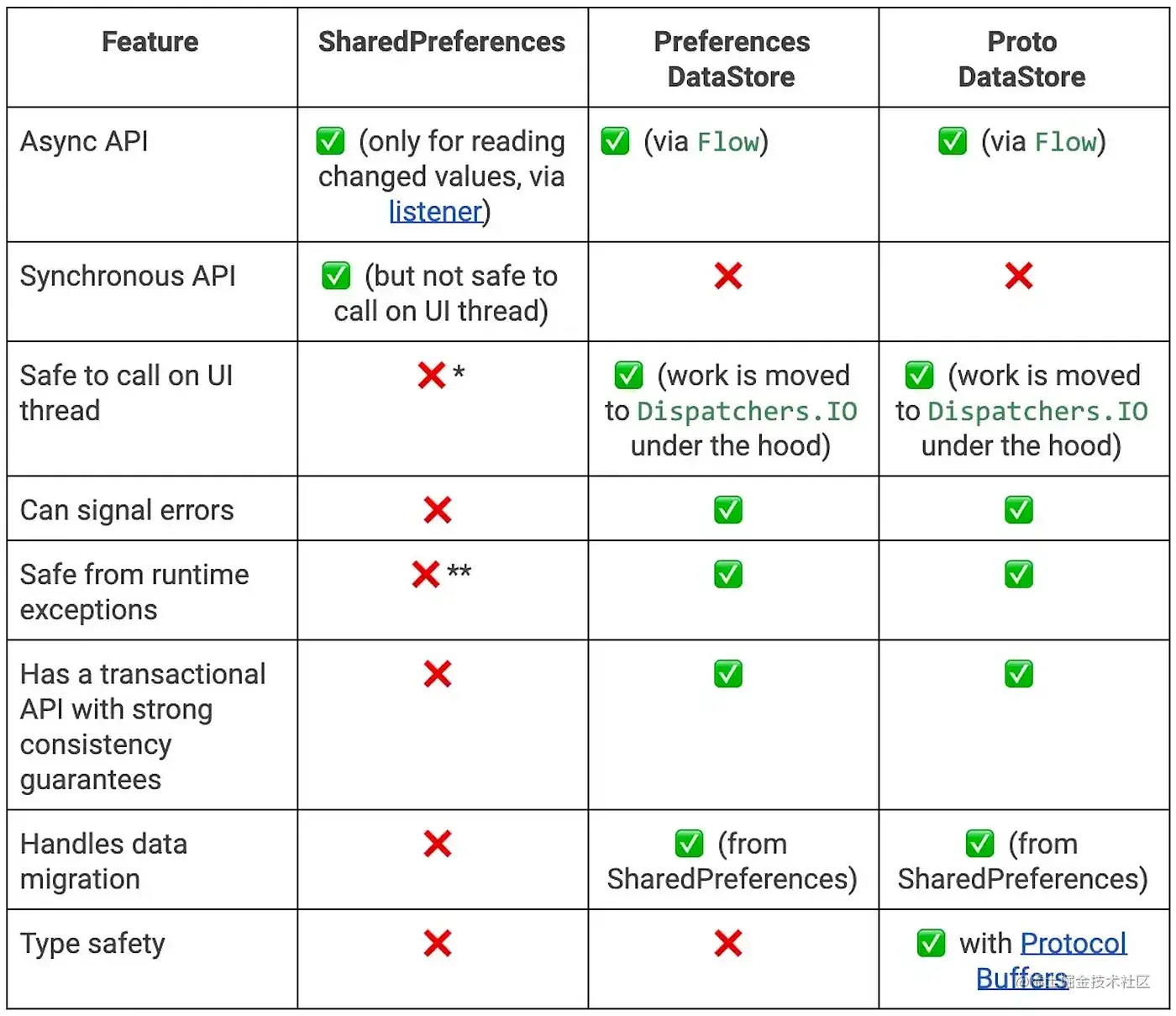
Recommendations:
- S̶h̶a̶r̶e̶d̶P̶r̶e̶f̶e̶r̶e̶n̶c̶e̶s̶
- DataStore
- EncryptedSharedPreferences
Testing
R8 Optimization
R8 is the default compiler that converts your project's Java bytecode into the DEX format used to run on the Android platform. It is a tool that helps us obfuscate and reduce our app code size by shortening class and property names, eliminating unused code and resources within the project. To learn more check the Android documentation about Shrinking, obfuscating, and optimizing your app.
- Code Shrinking
- Resource Shrinking
- Obfuscation
- Optimization
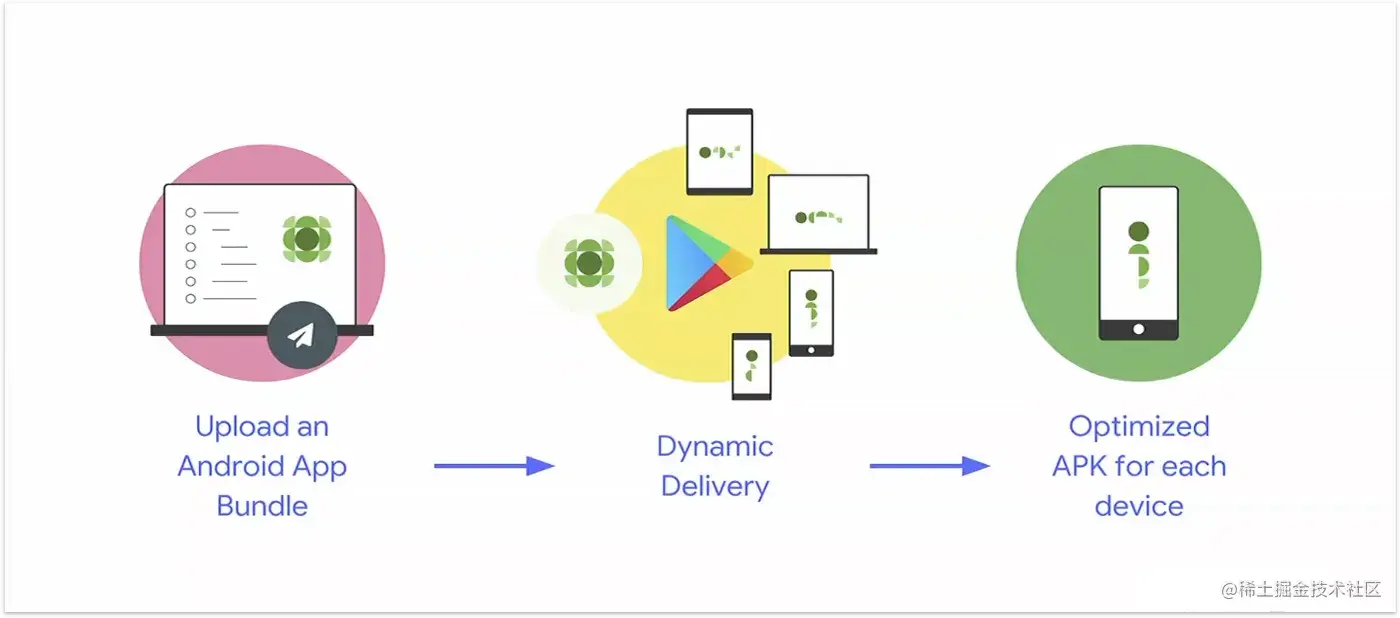
Play Feature Delivery
Google Play's app serving model, called dynamic delivery, uses Android App Bundles to build and serve optimized APKs for each user's device configuration, so users download only the code and resources they need to run your app.
Adaptive Layouts

With the growth of mobile devices used with different form factors, we need to have some tools to make our Android apps adaptable to different types of screens. This is why Android provides us with the Window Size Classes, in simple terms, it's three major screen format groups that mark key points for us to develop designs. This way we avoid the complexity of considering many screen designs, reducing our possibilities to three sets: Compat, Medium and Expanded.
Windows Size Classes
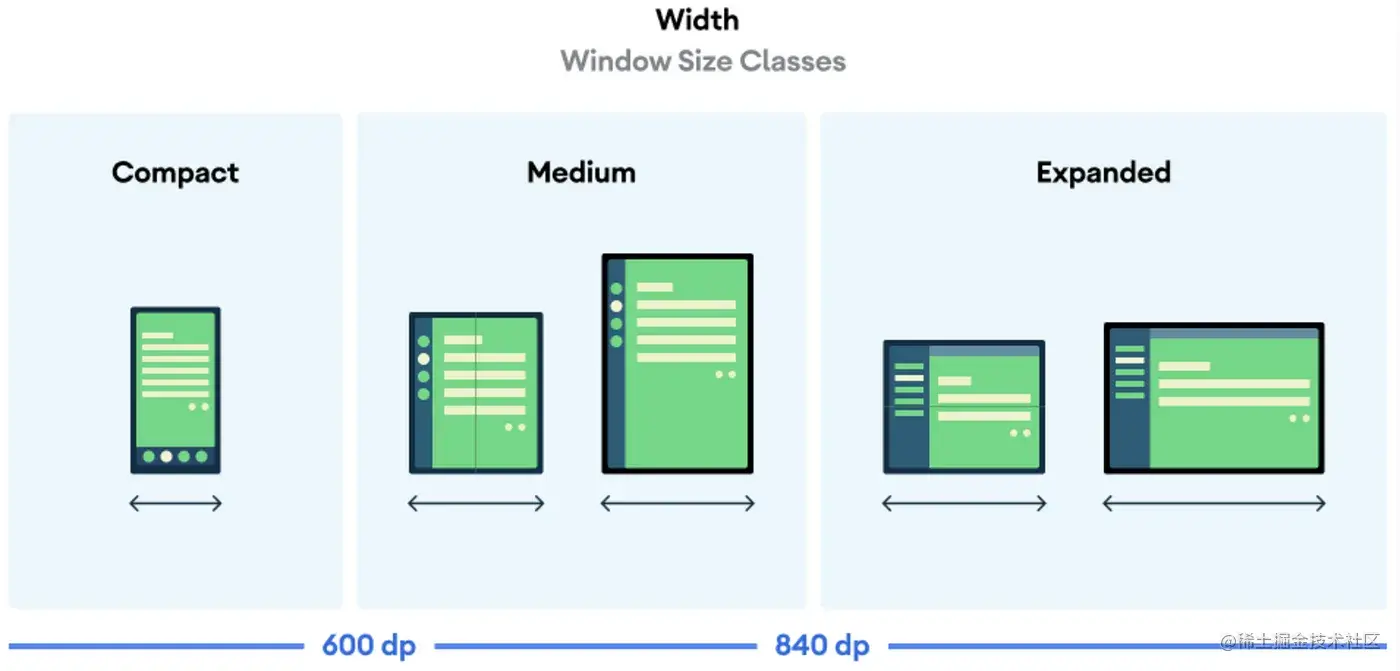
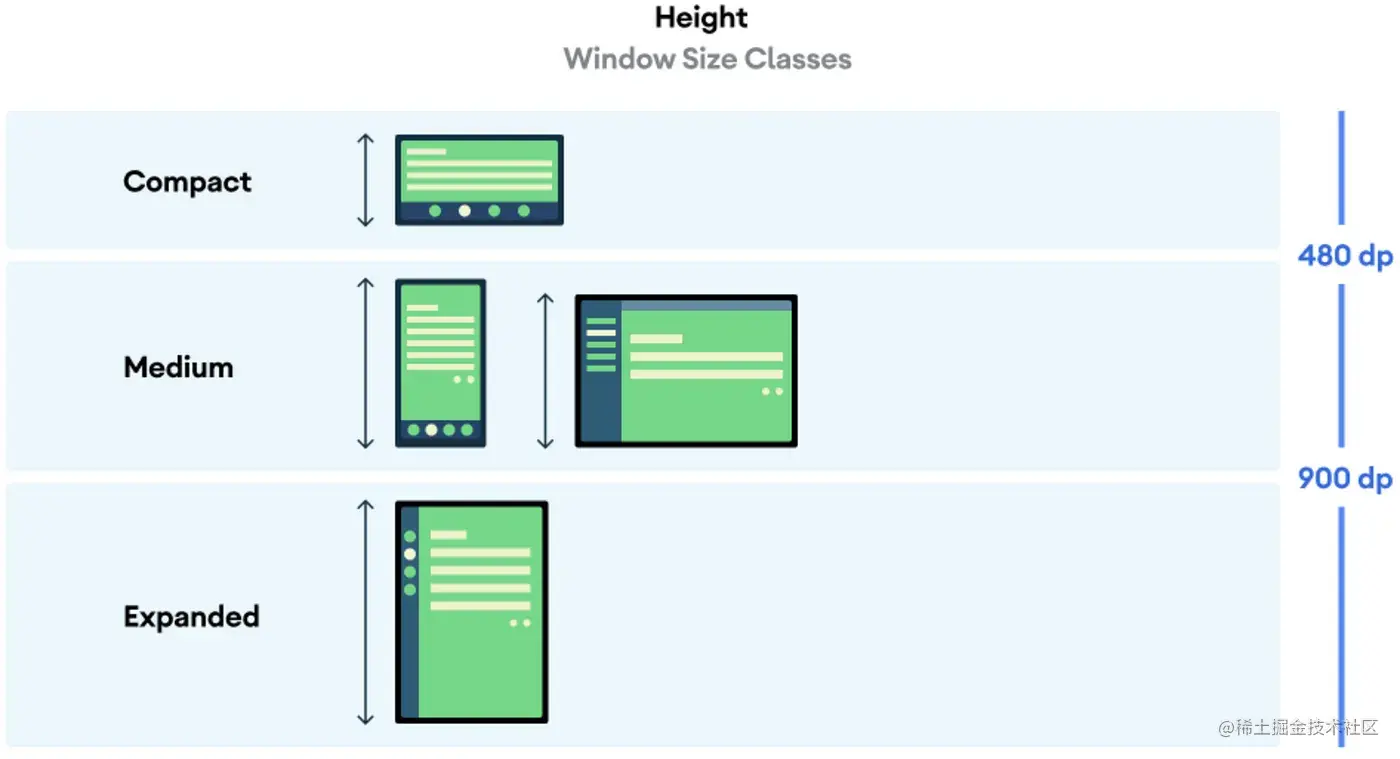
Support different screen sizes
Another important resource we have are Canonical Layouts, predefined screen designs that can be used for most scenarios in our Android apps, also showing us guidance on how to adapt them to large screens.

Other related resources
Form Factors at Google I/O 2022
Performance
When developing apps for Android we need to make sure the user experience is great, not only at the beginning of the app but through the entire execution. For this reason it's important to have some tools that allow us to do preventive analysis and continuous monitoring of situations that could impact the performance of the app, so here is a list of tools that can help you achieve that purpose:
In-app Updates
Keeping your users up-to-date with the latest version of your app on their devices allows them to try new features and benefit from performance improvements and bug fixes. While some users enable background updates when their device is connected to unmetered connectivity, other users may need a reminder to install updates. In-app updates is a Google Play Core Library feature that prompts active users to update your app without leaving your app or game, for convenience.
In-app updates is supported on devices running Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher. Additionally, in-app updates is only supported for Android mobile devices, Android tablets, and Chrome OS devices.
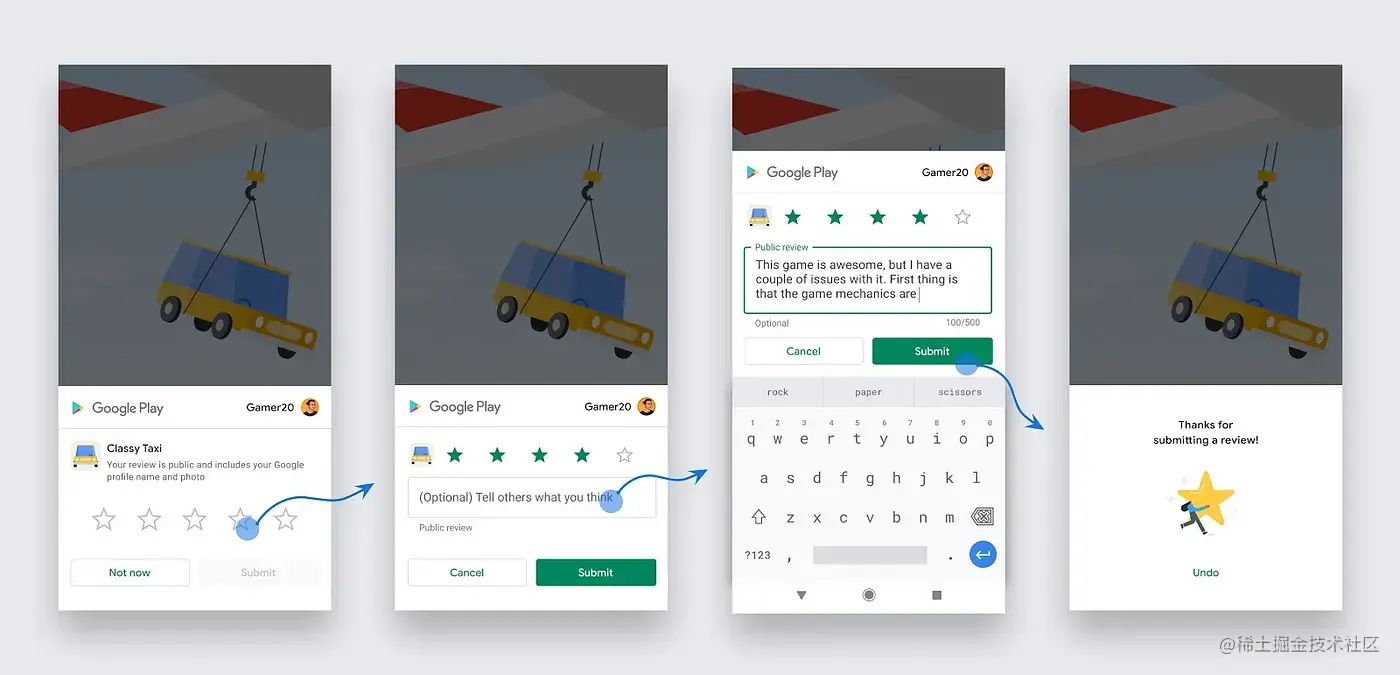
In-app Reviews
The Google Play In-app Review API allows you to prompt users to submit Play Store ratings and reviews without leaving your app or game, for convenience.
Generally, the in-app review flow can be triggered at any point in your app's user journey. During the flow, users can rate your app using a 1 to 5 stars system and add an optional written review. Once submitted, the review will be sent to the Play Store and eventually be made public.
To protect user privacy and prevent API misuse, your app should adhere to strict guidelines around when to request in-app reviews and review prompt design.
- In-app Reviews Documentation
Accessibility

Accessibility is an important feature of software design and building that, in addition to improving their user experience, provides the ability to use the application to people with accessibility needs. This concept aims to improve disabilities like people with vision impairments, color blindness, hearing issues, dexterity issues, and cognitive impairments among others.
Considerations:
- Increase text visibility (color contrast, adjustable text).
- Use large, simple controls.
- Describe each UI element.
Check Accessibility--Android Documentation
Security

Security is an aspect we must take into account when developing apps to safeguard device integrity, data security, and user trust; even it's the most important aspect, that's why I'm listing down a series of recommendations that will help you achieve that purpose.
- Encrypt sensitive data and files: Use EncryptedSharedPreferences and EncryptedFile.
- Apply signature-based permissions:
- When sharing data between apps you can control, use signature-based permissions.
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.myapp">
<permission android:name="my_custom_permission_name"
android:protectionLevel="signature" />
- Don't put the keys, tokens or sensitive data required for your app configuration directly on files or classes within the project libraries. Use local.properties instead.
Version Catalogs
Gradle provides a standard way to manage project dependencies centrally called version catalogs, introduced experimentally in version 7.0 and officially released in version 7.4.
The advantages are:
- For each catalog, Gradle generates type-safe accessors so you can easily add dependencies with auto-completion in your IDE.
- Each catalog is visible to all projects in a build. It's a central place you can declare the version of a dependency and ensure changes to that version apply across every subproject.
- Catalogs can declare dependency bundles which are commonly used "bundles" of dependencies.
- Catalogs can separate the group and name of a dependency from its actual version using version references, allowing a version declaration to be shared across multiple dependencies.
Logger
A logger is a software tool used to log information about a program's execution; important events, debug information, and other data that may be useful for diagnosing issues or understanding how a program is working. Loggers can be configured to write information to different locations like log files, console, database, or by sending the information to a logging server.
Linter

A linter is a programming tool used to analyze source code to find potential bugs or vulnerabilities in the code. These issues can be syntax errors, inappropriate coding styles, lack of documentation, security issues, etc. that can impact the quality and maintainability of the code.
Comments